Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications. spring-booter is a showcase project of Spring Boot to be used as a quick starter for creating a microservice application.
Customize SpringApplication using Builder
I close the command line properties for the applicaiton since it’s not safe for a released service in product environment.
new SpringApplicationBuilder().addCommandLineProperties(false).build().run(BooterApplication.class, args);
Using the SpringApplicationBuilder we can do lots of things to config SpringBootApplication class included set the banner off.
Change the Banner
I also change the default banner with my banner as below:
The application will search ‘banner.gif’, ‘banner.jpg’ and ‘banner.png’ in the Classpath, and then check ‘banner.txt’ file. If spring find nothing, using the default banner.
So I just put the banner.txt file in the Classpath to replace the banner.
Logback
Spring Boot uses Commons Logging for all logging, and default configurations for underlying log implementation are provided for Java Util Logging, Log4J2 and ‘Logback’. If we use the ‘Starter’, Logback will be used for logging. So I put a logback.xml in the Classpath.
SSL
First, we need to generate a keystore via keytool command, and put the file in the Classpath.
SSL can be configured by setting the various server.ssl.* properites, typically in applicaiton.properities.
server.ssl.key-store = classpath:keystore.p12
server.ssl.key-store-password = zhiyuan
server.ssl.keyStoreType: PKCS12
server.ssl.keyAlias: tomcat
And we need transfer the HTTP to HTTPS by using the code:
@Value("${server.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${server.http.port}")
private int http_port;
@Bean
public EmbeddedServletContainerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcat = new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
@Override
protected void postProcessContext(Context context) {
SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint();
securityConstraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL");
SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection();
collection.addPattern("/*");
securityConstraint.addCollection(collection);
context.addConstraint(securityConstraint);
}
};
tomcat.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(initiateHttpConnector());
return tomcat;
}
private Connector initiateHttpConnector() {
Connector connector = new Connector("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
connector.setScheme("http");
connector.setPort(http_port);
connector.setSecure(false);
connector.setRedirectPort(port);
return connector;
}
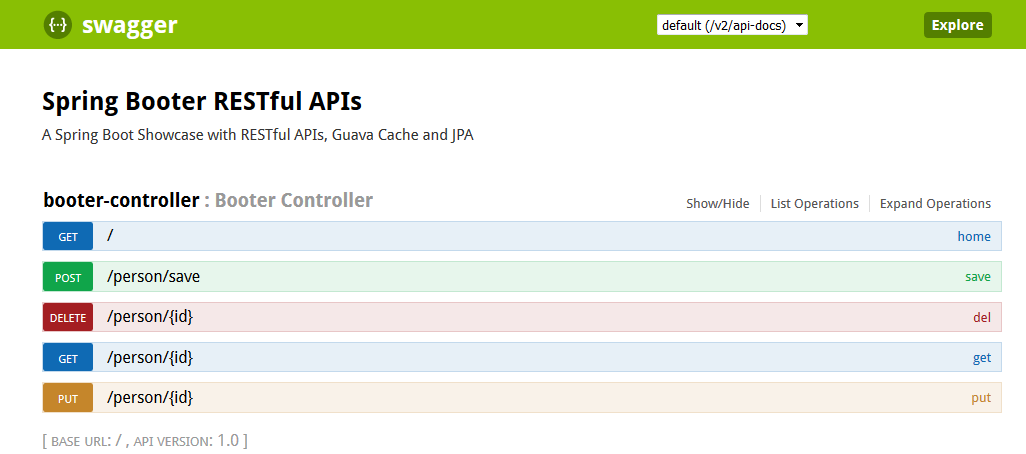
Swagger-UI
Swagger is a powerful open source framework backed by a large ecosystem of tools that helps you design, build, document, and consume your RESTful APIs.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
We also need a config class to make Swagger work.
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("me.zhiyuan.spring.booter.web")) //the package path of controller class
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Booter RESTful APIs")
.description("A Spring Boot Showcase with RESTful APIs, Guava Cache and JPA")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://zhiyuanma.github.io/")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
After this, forward to the URL – http://localhost:8000/swagger-ui.html
Guava cache
The cache abstraction does not provide an actual store and relies on abstraction materialized by the org.springframework.cache.Cache and org.springframework.cache.CacheManager interfaces.
Spring Boot auto-configures a suitable CacheManager according to the implementation as long as the caching support is enabled via the @EnableCaching annotation. In general, we do not need to tell Spring Boot which CacheManager to use, just put the dependency in the pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>20.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
Now Spring Boot will use Google Guava to provide caching service.
There are 3 annotations, Cacheable, CachePut and CacheEvict.
Cacheable for the simple select method, CachePut for the update or add method and CacheEvict for the delete method.
All of them need a attribute value which indicate the cache-names in the application.properties, and attribute key for the keyword in the cache, I set the same keyword in my code to make the cache work better.
You can check out the whole codes from here.